Sepanjang Invasi ke Irak, AS Gunakan Bom Uranium Untuk Hancurkan Generasi
http://www.eramuslim.com/berita/dunia-islam/sepanjang-invasi-ke-irak-as-gunakan-bom-uranium-untuk-hancurkan-generasi.htm#.UNLThawyqSo
Redaksi 1 – Kamis, 6 Safar 1434 H / 20 Desember 2012 07:40 WIB
Menurut
majalah Jerman “Der Spiegel” bahwa meskipun perang mesin AS di Irak
selama bertahun-tahun sudah sepi, akan tetapi di Basra dan Fallujah
mencatat peningkatan tajam dalam kasus penyakit cacat dan kanker, dan
beberapa peneliti mengungkapkan itu karena terdapat uranium yang
terkandung dalam amunisi yang digunakan militer AS selama invasi di
Irak.
Kantor berita “timur tengah” mengutip dari majalah tersebut bahwa
Perang Teluk pertama tahun 1991 mengakibatkan kasus kanker, tapi
jumlahnya tidak seperti dampak dari peperangan AS di Irak pada 2003 yang
melanda seluruh negeri dan sebab pasukan Amerika gunakan senjata yang
mengandung uranium, sehingga efek radiasi ledakan itu menyebabkan
penyakit tersebut.
Majalah ini melihat tingginya tingkat cedera dan cacat lahir di Basra
lebih besar dari yang lain, dan mengutip bahwa 200 Ton amunisi yang
mengandung uranium digunakan selama terjadi pertempuran.
majalah tersebut menggambarkan bahwa Amerika Serikat tidak memberikan
informasi apapun kepada media untuk mempublikasikan bahwa akan ada
gangguan genetik yang terjadi di Fallujah akibat amunisi uranium yang
digunakan oleh pasukan AS sepanjang agresi di Irak.
(za/al arabiya)
History of the Atomic Bomb & The Manhattan Project
My God, what have we done?" - Robert Lewis co-pilot of the Enola Gay
Atomic Bomb Explosion
Courtesy Outlawlabs

- Atomic Bomb ExplosionCourtesy Outlawlabs
http://inventors.about.com/od/astartinventions/a/atomic_bomb.htm
On August 2, 1939, just before the beginning of World War II,
Albert Einstein
wrote to then President Franklin D. Roosevelt. Einstein and several
other scientists told Roosevelt of efforts in Nazi Germany to purify
uranium-235, which could be used to build an atomic bomb. It was shortly
thereafter that the United States Government began the serious
undertaking known then only as "The Manhattan Project." Simply put, the
Manhattan Project was committed to expediting research that would
produce a viable atomic bomb.
Making Enriched Uranium
The most complicated issue to be addressed in making of an atomic bomb
was the production of ample amounts of "enriched" uranium to sustain a
chain reaction. At the time, uranium-235 was very hard to extract. In
fact, the ratio of conversion from uranium ore to uranium metal is
500:1. Compounding this, the one part of uranium that is finally refined
from the ore is over 99% uranium-238, which is practically useless for
an atomic bomb. To make the task even more difficult, the useful U-235
and nearly useless U-238 are isotopes, nearly identical in their
chemical makeup. No ordinary chemical extraction method could separate
them; only mechanical methods could work.
A massive enrichment laboratory/plant was constructed at Oak Ridge,
Tennessee. Harold Urey and his colleagues at Columbia University devised
an extraction system that worked on the principle of gaseous diffusion,
and
Ernest Lawrence
(inventor of the Cyclotron) at the University of California in Berkeley
implemented a process involving magnetic separation of the two
isotopes.
Next, a gas centrifuge was used to further separate the lighter U-235
from the heavier, non-fissionable U-238. Once all of these procedures
had been completed, all that needed to be done was to put to the test
the entire concept behind atomic fission ("splitting the atom," in
layman's terms).
Robert Oppenheimer - Manhattan Project
Over the course of six years, from 1939 to 1945, more than $2 billion
was spent during the history of the Manhattan Project. The formulas for
refining uranium and putting together a working atomic bomb were created
and seen to their logical ends by some of the greatest minds of our
time. Chief among the people who unleashed the power of the atom was
Robert Oppenheimer, who oversaw the project from conception to completion.
Testing The Gadget aka Atomic Bomb
Finally, the day came when all at Los Alamos would find out if "The
Gadget" (code-named as such during its development) was going to be the
colossal dud of the century or perhaps an end to the war. It all came
down to a fateful morning in midsummer, 1945.

At 5:29:45 (Mountain War Time) on July 16, 1945, in a white blaze that
stretched from the basin of the Jemez Mountains in northern New Mexico
to the still-dark skies, "The Gadget" ushered in the Atomic Age. The
light of the explosion
then turned orange as the atomic fireball began shooting upwards at 360
feet per second, reddening and pulsing as it cooled. The characteristic
mushroom cloud of radioactive vapor materialized at 30,000 feet.
Beneath the cloud, all that remained of the soil at the blast site were
fragments of jade green radioactive glass created by the heat of the
reaction.
The brilliant light from the detonation pierced the early morning skies
with such intensity that residents from a faraway neighboring community
would swear that the sun came up twice that day. Even more astonishing
is that a blind girl saw the flash 120 miles away.
Upon witnessing the explosion, its creators had mixed reactions. Isidor
Rabi felt that the equilibrium in nature had been upset as if humankind
had become a threat to the world it inhabited. Robert Oppenheimer,
though ecstatic about the success of the project, quoted a remembered
fragment from the Bhagavad Gita. "I am become Death," he said, "the
destroyer of worlds." Ken Bainbridge, the test director, told
Oppenheimer, "Now we're all sons of bitches."
After viewing the results several participants signed petitions against
loosing the monster they had created, but their protests fell on deaf
ears. The Jornada del Muerto of New Mexico would not be the last site on
planet Earth to experience an atomic explosion.
Key Staff - Manhattan Project
Scientists Who Invented the Atomic Bomb under the Manhattan Project:
Robert Oppenheimer,
David Bohm,
Leo Szilard, Eugene Wigner, Otto Frisch, Rudolf Peierls, Felix Bloch,
Niels Bohr, Emilio Segre, James Franck,
Enrico Fermi,
Klaus Fuchs and
Edward Teller. View a copy of the
letter Einstein wrote Roosevelt that prompted the Manhattan Project.


 |
 |
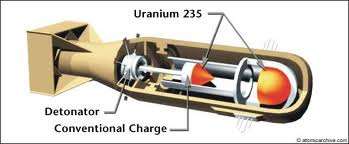
Uranium bomb
The aim of all nuclear bomb designers is to create a supercritical mass
which will sustain a chain reaction and violently release vast amounts
of heat.
One of the simplest is a so-called 'gun' design.
Here, a smaller subcritical mass is fired at a larger one, causing the
combined mass to go supercritical triggering a nuclear explosion.
The process occurs in less than a second.
To make fuel for a uranium bomb, highly-enriched uranium hexafluoride is
first converted into uranium oxide, and then uranium metal ingots.
This can be done using relatively simple chemical and engineering processes.
The most powerful basic fission weapon - an atom bomb - will detonate with an explosion the force of 50 kilotons.
This force can be increased by a technique called boosting, which harnesses the properties of nuclear fusion.
Fusion consists of the joining together of the nuclei of atoms of
hydrogen isotopes to produce nuclei of helium. This process occurs when
hydrogen nuclei are subjected to intense heat and pressure, both of
which are produced by a nuclear bomb.
Nuclear fusion has the effect of injecting more energetic neutrons into the fission reaction, resulting in a bigger explosion.
Such fission-fusion-fission devices are known as hydrogen bombs, or thermonuclear weapons.
-
Depleted Uranium -
The Real Dirty Bombs
By Christopher Bollyn
8-27-4
http://rense.com/general56/dep.htm
-
-

-
-
 
  
  -
- Lost in the media circus about the Iraq war, supposedly
being fought to prevent a tyrant from obtaining weapons of mass destruction,
is the salient fact that the United States and Britain are actively waging
chemical and nuclear warfare in Iraq - using depleted uranium munitions.
-
- The corporate-controlled press has failed to inform the
public that, in spite of years of UN inspections and numerous international
treaties, tons of banned weapons of mass destruction (WMD) - used and unused
- remain in Iraq. Indeed, both chemical and radioactive WMD have been -
and continue to be used against U.S. and coalition soldiers.
-
- The media silence surrounding these banned WMD, and the
horrendous consequences of their use, is due to the simple fact that they
are being used by the U.S.-led coalition. They are the new "Silver
Bullet" in the U.S. arsenal. They are depleted uranium weapons.
-
- Depleted uranium (DU) weapons were first used during
the first Gulf War against Iraq in 1991. The Pentagon estimated that between
315 and 350 tons of DU were fired during the first Gulf War. During the
2003 invasion and current occupation of Iraq, U.S. and British troops have
reportedly used more than five times as many DU bombs and shells as the
total number used during the 1991 war.
-
- While the use of DU weapons and their effect on human
health and the environment are subjects of extreme importance the Pentagon
is noticeably reluctant to discuss these weapons. Despite numerous calls
to specific individuals identified as being the appointed spokesmen on
the subject, not one would answer their phone during normal business hours
for the purpose of this article.
-
- Dr. Doug Rokke, on the other hand, former director of
the U.S. Armyís Depleted Uranium Project, is very willing to talk
about the effects of DU. Rokke was involved in the "clean up"
of 34 Abrams tanks and Bradley armored vehicles hit by friendly fire during
the 1991 Gulf War. Today he suffers from the ill effects of DU in his body.
-
- Rokke told American Free Press that the Pentagon uses
DU weapons because they are the most effective at killing and destroying
everything they hit. The highest level of the U.S. and British governments
have "totally disregarded the consequences" of the use of DU
weapons, Rokke said.
-
- The first Gulf War was the largest friendly fire incident
in the history of American warfare, Rokke says. "The majority of the
casualties were the result of friendly fire," he told AFP.
-
- DU is used in many forms of ammunition as an armor penetrator
because of its extreme weight and density. The uranium used in these missiles
and bombs is a by-product of the nuclear enrichment process. Experts say
the Department of Energy has 100 million tons of DU and using it in weapons
saves the government money on the cost of its disposal.
-
- Rather than disposing of the radioactive waste, it is
shaped into penetrator rods used in the billions of rounds being fired
in Iraq and Afghanistan. The radioactive waste from the U.S. nuclear weapons
industry has, in effect, been forcibly exported and spread in the environments
of Iraq, Afghanistan, the former Yugoslavia, Puerto Rico, and elsewhere.
-
- THE REAL "DIRTY BOMBS"
-
- "A flying rod of solid uranium 18-inches long and
three-quarters of an inch in diameter," is what becomes of a DU tank
round after it is fired, Rokke said. Because Uranium-238 is pyrophoric,
meaning it burns on contact with air, DU rounds are burning as they fly.
-
- When the DU penetrator hits an object it breaks up and
causes secondary explosions, Rokke said. "It's way beyond a dirty
bomb," Rokke said, referring to the terror weapon that uses conventional
explosives to spread radioactive material.
-
- Some of the uranium used with DU weapons vaporizes into
extremely small particles, which are dispersed into the atmosphere where
they remain until they fall to the ground with the rain. As a gas, the
chemically toxic and radioactive uranium can easily enter the body through
the skin or the lungs and be carried around the world until it falls to
earth with the rain.
-
- AFP asked Marion Falk, a retired chemical physicist who
built nuclear bombs for more than 20 years at Lawrence Livermore lab, if
he thought that DU weapons operate in a similar manner as a dirty bomb.
"That's exactly what they are," Falk said. "They fit the
description of a dirty bomb in every way."
-
- According to Falk, more than 30 percent of the DU fired
from the cannons of U.S. tanks is reduced to particles one-tenth of a micron
(one millionth of a meter) in size or smaller on impact.
-
- "The larger the bang" the greater the amount
of DU that is dispersed into the atmosphere, Falk said. With the larger
missiles and bombs, nearly 100 percent of the DU is reduced to radioactive
dust particles of the "micron size" (virus size -ed) or smaller,
he said.
-
- While the Pentagon officially denies the dangers of DU
weapons, since at least 1943 the military has been aware of the extreme
toxicity of uranium dispersed as a gas (or dust particles -ed).
-
- A declassified memo written by James B. Conant and two
other physicists working on the U.S. nuclear project during the Second
World War, and sent to Brig. Gen. L.R. Groves on October 30, 1943, provides
the evidence:
-
- "As a gas warfare instrument the [radioactive] material
would be ground into particles of microscopic size to form dust and smoke
and distributed by a ground-fired projectile, land vehicles, or aerial
bombs," the 1943 memo reads.
-
- "In this form it would be inhaled by personnel.
The amount necessary to cause death to a person inhaling the material is
extremely small. It has been estimated that one millionth of a gram accumulation
in a personís body would be fatal. There are no known methods of
treatment for such a casualty."
-
- The use of radioactive materials "as a terrain contaminant"
to "deny terrain to either side except at the expense of exposing
personnel to harmful radiations" is also discussed in the Groves memo
of 1943.
-
- "Anybody, civilian or soldier, who breathes these
particles has a permanent dose, and itís not going to decrease very
much over time," Leonard Dietz, a retired nuclear physicist with 33
years experience told the New York Daily News. "In the long run -
veterans exposed to ceramic uranium oxide have a major problem."
-
- "Inhaled particles of radioactive uranium oxide
dust will either lodge in the lungs or travel through the body, depending
on their size. The smallest particles can be carried through cell walls
and "affect the master code - the _expression of the DNA," Falk
told AFP.
-
- Inhaled DU can "fool around with the keys"
and do damage to "practically anything," Falk said. "It
affects the body in so many ways and there are so many different symptoms
that they want to give it different names," Falk said about the wide
variety of ailments afflicting Gulf War veterans.
-
- Today, more than one out of every three veterans from
the first Gulf War are permanently disabled. Terry Jemison of the Dept.
of Veterans Affairs said that of the 592,561 discharged veterans from the
1991 war in Iraq, 179,310 are receiving disability compensation and another
24,763 cases are pending.
-
- The "epigenetic damage" done by DU has resulted
in many grossly deformed children born in areas such as southern Iraq where
tons of DU have contaminated the environment and local population. An untold
number of Americans have also been born with severe birth defects as a
result of DU contamination.
-
- The New York Daily News conducted a study on nine recently
returned soldiers from the New York National Guard. Four of the nine were
found to have "almost certainly" inhaled radioactive dust from
exploded DU shells.
-
- Laboratory tests revealed two manmade forms of uranium
in urine samples from four of the 9 soldiers. The four soldiers are the
first confirmed cases of inhaled DU from the current Iraq war.
-
- "These are amazing results, especially since these
soldiers were military police not exposed to the heat of battle,"
said Dr. Asaf Duracovic, who examined the soldiers and performed the testing.
"Other American soldiers who were in combat must have more DU exposure,"
Duracovic said. Duracovic is a colonel in the Army reserves and served
in the 1991 Gulf War.
-
- The test results showing that four of nine New York guardsmen
test positive for DU "suggest the potential for more extensive radiation
exposure among coalition troops and Iraqi civilians," the Daily News
reported.
-
- "A large number of American soldiers [in Iraq] may
have had significant exposure to uranium oxide dust," Dr. Thomas Fasey,
a pathologist at Mount Sinai Medical Center and an expert on depleted uranium
said, "And the health impact is worrisome for the future."
-
- HOTTER THAN HELL
-
- "I'm hotter than hell," Rokke told AFP. The
Dept. of Energy tested Rokke in 1994 and found that he was excreting more
than 5,000 times the permissible level of depleted uranium. Rokke, however,
was not informed of the results until 1996.
-
- As director of the Depleted Uranium Project in 1994-95,
Rokke said his task was three fold: determine how to provide medical care
for DU victims, how to clean it up, and how to educate and train personnel
using DU weapons.
-
- Today, Rokke says that DU cannot be cleaned up and there
is no medical care. "Once you're zapped - you're zapped," Rokke
said. Among the health problems Rokke is suffering as a result of DU contamination
is brittle teeth. He said that he just paid out $400 for an operation for
teeth that have broken off. "The uranium replaces the calcium in your
teeth and bones," Rokke said.
-
- "You fight for medical care every day of your life,"
he said.
-
- "There are over 30,000 casualties from this Iraq
war," Rokke said.
-
- The three tasks set out for the Depleted Uranium Project
have all failed, Rokke said. He wants to know why medical care is not being
provided for all the victims of DU and why the environment is not being
cleaned up.
-
- "They have to be held accountable," Rokke said,
naming President George W. Bush, Secretary of Defense Donald Rumsfeld,
and British prime minister Tony Blair. They chose to use DU weapons and
"totally disregarded the consequences."
-
- Christopher Bollyn
|
|
 |
|





Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar